- They sense the amount of water flow across the pipeline and dose the exact amount of chemical required according to the flow.
- A wide range of chemicals can be used as they are made of non-corrosive and non- reactive HDPE materials.
- They have an inbuilt level controller which can shut the pump if the chemical level goes below the set point. This saves the pump from running dry.
- As they are completely electronic a high level of accuracy of dosing is maintained.
- As they are light and compact in construction they can be easily mounted in a matter of minutes in any place and even on walls
- 95% - 99% of the TDS
- 99% of the organics (including pyrogens) and bacteria
- The feed water temperature
- Total Dissolved Solids in feed water ( TDS )
- Operating pressure and the over all recovery of the system.
RO CROSS FLOW FILTERATION
- Polypropylene – They are made up of high quality of PVC / HDPE
- Stainless Steel (304 / 316) – These housing are used mainly in Mineral water production and places were they need high quality, high pure water like pharmaceutical industries, etc
- Spun type – They are used for normal filteration and do not have a long life.
- Wound type – They are used for filtering water with high turbidity as their surface area, and dirt holding capacity is more.
- Pleated type – These are high efficiency cartridges which can even stop bacteria and other pathogens which are present in the water. They have a long life of more than six months. The biggest advantage is that they are washable for any number of times.
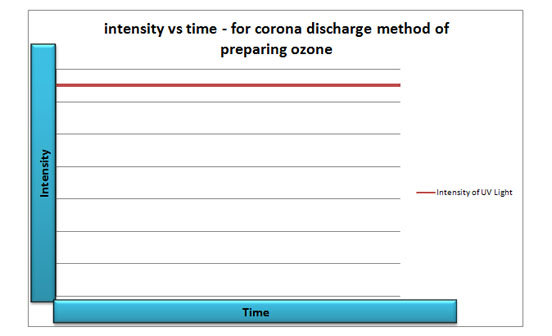
Intensity Vs Time
- Equalization tank / neutralization tank.
- Air blower.
- Primary clarifier tank
- Alum dosing tank
- Alum dosing system
- Lime Dosing Tank
- Lime dosing system
- Polymer Dosing tank
- Polymer dosing system
- Aeration tank with diffusers
- Secondary clarifier tank with sludge recycle
- Sludge drying beds
- Chlorine contact Tank/Clarified Water Storage Tank
- Chlorine dosing tank
- Filter Feed Pump.
- Pressure Sand Filter
- Activated Carbon Filter
- Reverse Osmosis (Stage I)
- Reverse Osmosis (Stage II)
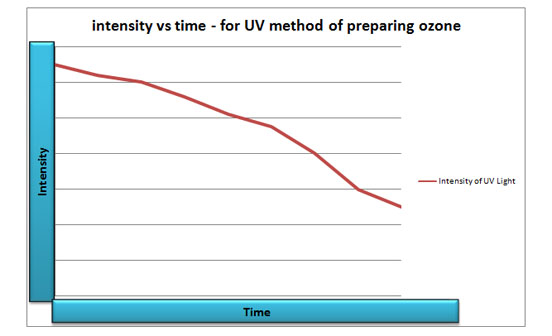
Intensity Vs Time
- The effluent from all the process involved in the industry is first collected in Equalization Tank / Neutralization tank.
- The Equalization Tank is provided with the bar screen to remove the coarse particles from the effluent & thus prevent the blockage / stoppage of the pump
- Since the effluent is alkaline in nature, ph correcting agent is added in Equalization Tank / neutralization tank for neutralizing the effluent with the help of dosing pump. The pH is adjusted to 6.5 – 6.8
- The neutralized effluent is then pumped with the help of effluent transfer pumps to Primary clarifier tank.
- In Primary clarifier tank-flocculating agents like alum, polymer, & lime is added.
- Flocs settled at the bottom of the primary clarifier tank & are then transfer to the sludge drying bed
- The clear supernatant from primary clarifier tank overflows to the Aeration Tank for biological treatment. The oxygen required for the bacterial growth is supplied through surface aerators.
- Mixed liquor along with degraded effluent is then overflows to the Secondary clarifier tank. The clarifier unit is provided to arrest the microbial sludge leaving from the system, as a particular concentration of the MLSS is to be maintained in the Aeration Tank.
- The sludge settles at the bottom of the clarifier tank & is pumped back with the help of sludge return pumps to the Aeration Tank to maintain required concentration.
- In case of excess sludge in the system, the recycle pumps will be used to drain the sludge, to the sludge drying beds.
- In case of excess sludge in the system, the recycle pumps will be used to drain the sludge, to the sludge drying beds.
- The clarified effluent is then fed to the Pressure Sand Filter & Activated Carbon Filter with the help of Filter Feed Pump
- Then it is passed through a Reverse Osmosis Unit (Stage I) and the treated water is collected in a common tank.
- The reject of the Stage I is passed through the Reverse Osmosis Unit (Stage II) to reduce the discharge effluent to Zero discharge level. The treated water is collected the same collection tank of the stage I.
SULLAGE TREATMENT
SEWAGE TREATMENT
ANAEROBIC FOLLOWED BY AEROBIC ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESSCOLLECTION / PRIMARY SETTLING TANK
ANAEROBIC TANK
AERATION TANK
HOPPER BOTTOM SETTLING TANK
CHLORINATION / DISINFECTION AND PRESSURE FILTERATION
SLUDGE TANK
ADVANTAGES – ANAEROBIC FOLLOWED BY AEROBIC SYSTEM FOR SEWAGE
- Process is Eco-friendly, only natural growth of microorganisms and air essential. The treatment is ensured by the natural growth of microbes to feed on the effluent.
- Consistent high quality of treated water
- Simple operation and less maintenance required as there is no submerged moving parts within the aeration tank.
- An automatic electrical control panel is provided.
- Compact Design.
- Neat and clean environment around the plant.
- Tanks can be kept underground and the area above utilized for other purposes.
CONSTRUCTION
- Systems are manufactured from MSRL, FRP, SS 316, Mild Steel etc
- Standard models are available for a flow rate of 50 LPH to 1,00,000 LPH.
- Custom made models also available as per requirements
- Use of excellent quality resin gives high output.
- The feed water temperature
- Total Dissolved Solids in feed water ( TDS )
- Operating pressure and the over all recovery of the system.
Process Treatment
Final Treatment
Automatic Bottle Filling Machine - Rinsing
Automatic Bottle Filling Machine - Filling
Bottle filling and capping machine
The Machine
The Preform Loader
The Preform Heater
The Rotation of preforms
Advantages
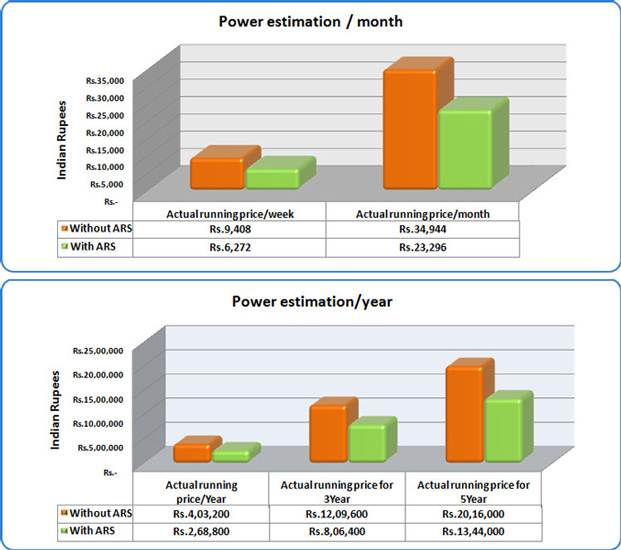
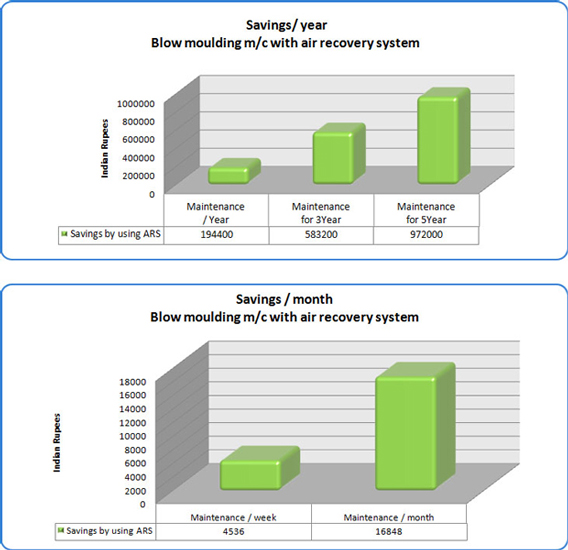
- Savings can exceed 50% of the original amount of air used by the bottle blowing process.
- Significant financial savings from the reduction in electricity consumption by the compressor.
- The possibility of installing new blowers without investing in new compressors, leading to savings in purchasing costs.
- The possibility of closing down some compressors, with resulting savings in maintenance costs.
- Noise reduction and space saving in your factory tanks to the lower number of compressors installed.
- You will recoup your investment in a short time, depending on electricity costs, bottle volume and production rates.
- Overall savings on production costs
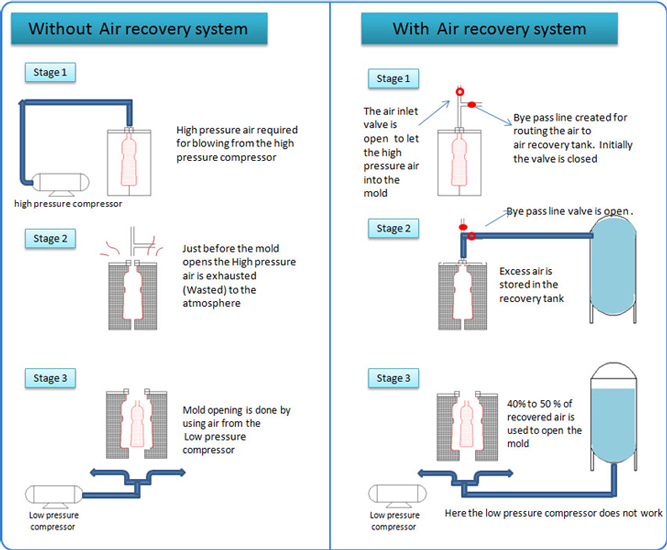
- PET bottles are blow molded by injecting High Pressure Air (at about 40 bars - 580 psi) into a mould.When the blow-off valve is opened, the air contained in the bottle is directed to a muffler which releases the air into the atmosphere. This means that all of the air is lost. With the ARS recovery system, the air is directed to a recycling reservoir (about 50%), where it will be re-used under pressure.
Plus Points Of ARS System
- The ARS System makes absolutely no difference to cycle times or the machine process. As a result, bottles can continue to be produced at the same rate without a drop in production or quality.
- The ARS System can be installed quickly, with no major modifications to the blower units. Installation must be carried out by a qualified technician.
- The ARS air recycling system can be disconnected without affecting the operation of the machine. The ARS System is completely independent of the blower unit, both mechanically and electrically.
- The ARS System is either managed mechanically or by its own electronic system, depending on the configuration of the blower unit.
- 2 CAVITY – 2400 BPH
- 3 CAVITY – 3000 BPH
- 4 CAVITY – 3800 BPH
- 6 CAVITY – 5000 BPH
Automatic Shrink Wrapping Machine
20 Ltrs Jar Fully Automatic Washing, Rinsing, Filling & Capping Machine.
Comparison between Manual Jar Washing & Automatic Jar Filling.
| Manual washing 100 Jars/Hr | 20 ltrs Jar Machine 100 Jars/Hr |
|---|---|
| Manual washing requires more than 6- 8 workers for washing the Jars alone. | Requires only 1 person to load the Jar onto the machines Conveyor. |
| Separate 2-3 workers are required for the Rinsing and Filling of the Jars. | This operation is completely automatic and Labour free. |
| Manual handling (like dropping, throwing, sliding, etc) of Jars at each point leads to breakage and less life of the Jars. | There is absolutely no manual handling of any jar, as jars move from one stage to another purely on a Conveyor belt. Hence life of jar increases. |
| Manual handling also leads to scratches and dents on the jar which reduces the look of the Jar. | No chance of scratches or any kind of dents possible during auto operation and hence enhances the life & looks |
| Wastage of water is huge and nothing is actually recycled. | Water usage is minimal and all water is recycled at every single stage. |
| Washing over a Time period is not exactly equal as during the start of the washing process. | As the system is automated the machine cleans all the jars equally on all counts. |
| Cost of labour is huge and if workers do not report on time there is loss of production & Revenue. | Cost is reduced as the unit requires only 3 workers & any one can opt to do the production, due to easy operation. |
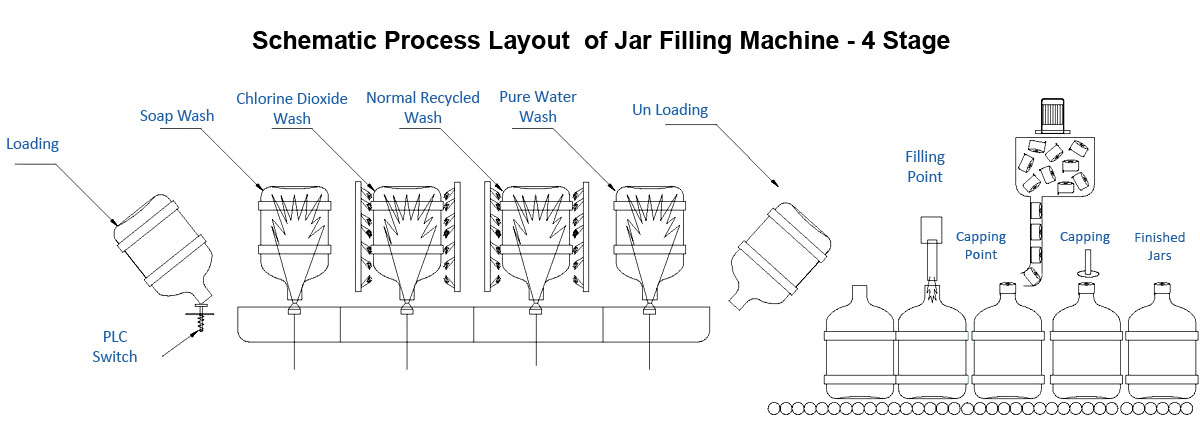
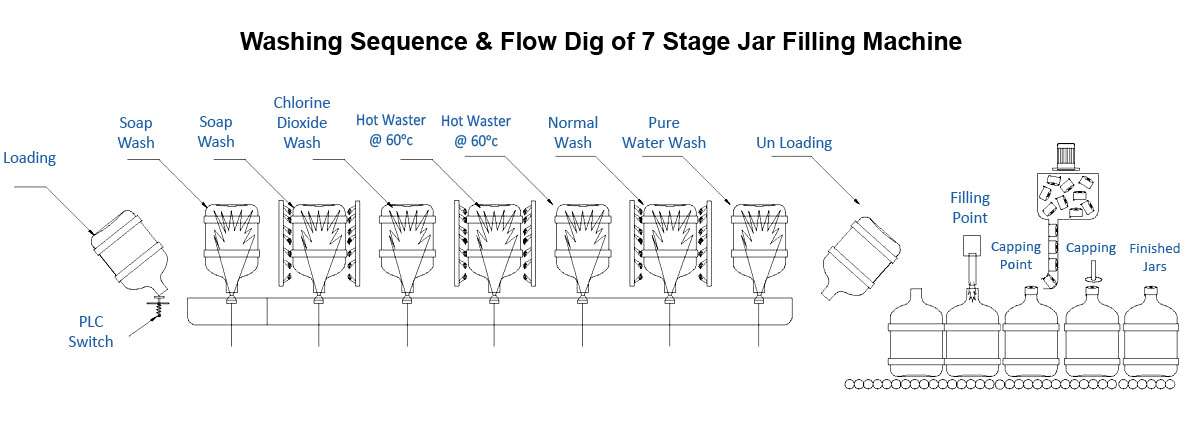
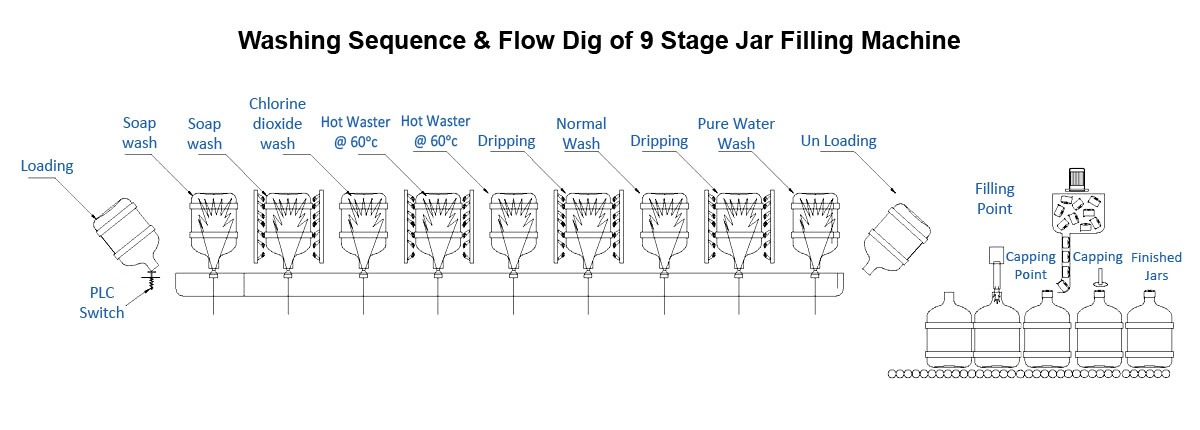
- Stage 1 – Alkali Water Wash
- Stage 2 – soap water wash
- Stage 3 – Disinfectant water Wash
- Stage 4 – Hot Water Wash – 1
- Stage 5 – Hot Water Wash – 2
- Stage 6 – Recycled Pure Water Wash
- Stage 7 – Final Product Water wash
Automatic Labeling
Specifications:
- Materials: stainless steel and high quality aluminum alloy
- Compact structure
- No need to fasten feet bolts to ground, it can be moved flexibly
- Shrinking film volume label frame: adjustable according to different volume label paper pipes from 5 to 10
- Gear device can be adjusted conveniently without using tools, which makes it suitable for different bottles
- Servo motor and high-delicacy photo-electricity from Japan make the cutting label precise